深度和广度优先遍历
深度和广度优先遍历
该文记录深度和广度优先遍历的主要思想。
深度和广度优先遍历
1 深度优先遍历
1.1 定义
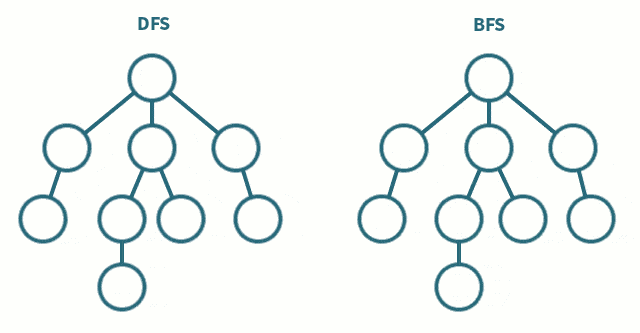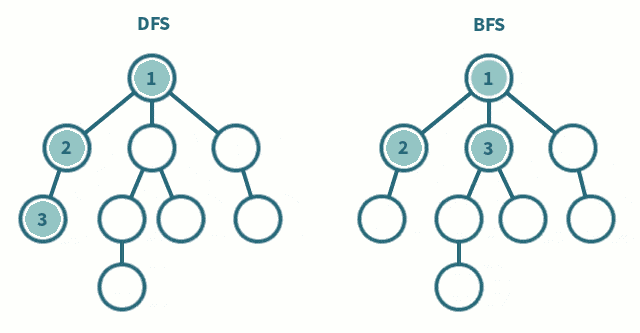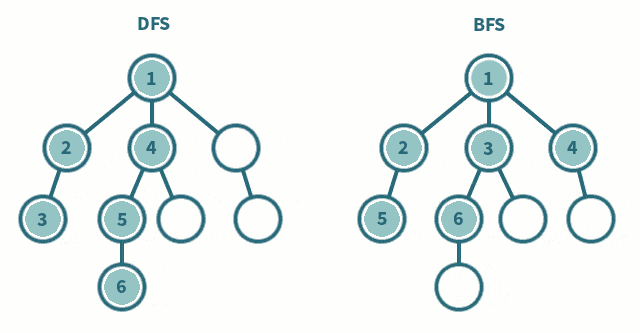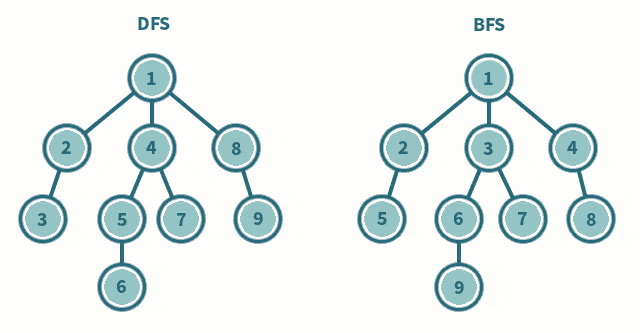
深度优先搜索算法(Depth-First-Search,DFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索 树 或 图 的算法。
这个算法会尽可能深地搜索树的分支。当节点v的所在边e都己被探寻过,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。这一过程一直进行到已发现从源节点可达的所有节点为止。如果还存在未被发现的节点,则选择其中一个作为源节点并重复以上过程,整个进程反复进行直到所有节点都被访问为止。
1.2 适用场景
- 多源DFS(求全部方案)
2 广度优先遍历
2.1 定义
广度优先搜索算法(Breadth-First-Search,BFS)是一种 图形 搜索算法。
简单的说,BFS是从根节点开始,沿着树的宽度遍历树的节点。如果所有节点均被访问,则算法中止。
2.2 适用场景
- 层序遍历
- 最短路径(没有权重)
3 区别
3.1 图例
3.2 优缺点
DFS 可以使用 栈(stack) 和 递归 两种方式实现,为了节省空间一般使用递归实现,这样导致容易堆栈溢出(递归深度不能太深)。
BFS 一般使用 队列(queue) 实现, BFS在搜索过程中需要保存搜索过的状态,而且一般情况需要一个队列来记录,这样空间需求比较大。
4 示例
4.1 DFS
- 递归实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
/**
* @brief 深度优先遍历
* - 把和 image[sr, sc] 颜色一样的且相邻的修改为新颜色
*/
class Solution
{
public:
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; // 上,右,下,左
const int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int newColor)
{
// 栈 保存遍历状态
stack<pair<int, int>> sta;
// 初始数据
if (image[sr][sc] != newColor)
{
sta.emplace(sr, sc);
}
int oldColor = image[sr][sc];
while (!sta.empty())
{
int x = sta.top().first;
int y = sta.top().second;
sta.pop();
if (oldColor == image[x][y])
{
image[x][y] = newColor;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int mx = x + dx[i];
int my = y + dy[i];
if (mx >= 0 && mx < image.size() && my >= 0 && my < image[0].size())
{
// 更新数据
sta.emplace(mx, my);
}
}
}
}
return image;
}
};
- 栈实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* @brief 递归法
*/
class Solution
{
public:
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; // 上,右,下,左
const int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int newColor)
{
if (image[sr][sc] != newColor)
{
DFS(image, sr, sc, image[sr][sc], newColor);
}
return image;
}
void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int oldColor, int newColor)
{
if (oldColor == image[sr][sc])
{
image[sr][sc] = newColor;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int mx = sr + dx[i];
int my = sc + dy[i];
if (mx >= 0 && mx < image.size() && my >= 0 && my < image[0].size())
{
DFS(image, mx, my, oldColor, newColor);
}
}
}
}
};
733. 图像渲染
4.2 BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
/**
* @brief 广度优先遍历,有记录
*/
class Solution
{
public:
const int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; // 上,右,下,左
const int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid)
{
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> dist(m, vector<int>(n));
vector<vector<int>> seen(m, vector<int>(n));
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
// 遍历记录腐烂橘子位置
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (2 == grid[i][j])
{
que.emplace(i, j);
seen[i][j] = 1;
}
}
}
// 广度优先遍历
while (!que.empty())
{
int x = que.front().first;
int y = que.front().second;
que.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int mx = x + dx[i];
int my = y + dy[i];
if (mx >= 0 && mx < m && my >= 0 && my < n && 1 == grid[mx][my] && 0 == seen[mx][my])
{
dist[mx][my] = dist[x][y] + 1; // 时间 +1
seen[mx][my] = 1; // 记录遍历过
que.emplace(mx, my); // 添加腐烂橘子位置
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (1 == grid[i][j] && 0 == dist[i][j])
{
return -1;
}
res = max(dist[i][j], res);
}
}
return res;
}
};
994. 腐烂的橘子
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权