STL 图解
- STL 图解
- 参考
本文介绍 STL 实现流程。
STL 图解
STL 包含五种主要组件:
- 算法(algorithm):定义计算过程。
- 容器(container):管理一组内存位置。
- 迭代器(iterator):提供算法遍历容器的方法。
- 函数对象(function object):将函数封装在对象中,供其他组件使用。
- 适配器(adaptor):调整组件以提供不同的接口。
从实现来看还需要包含:
- 分配器(allocator):用于处理容器对内存的分配与释放请求。
以下分析适用于 GCC9 。
1. 源码阅读
1.1. ::template
在 __rebind 函数体中,在 :: 后面有个 template 关键字,这是用于告诉编译器 template 后面的 < 不是比较符号,而是模板参数符号。就是类似于 _Tp 前面的 typename 是告诉编译器 :: 后面的是类成员函数,而不是 static 函数。
1
using type = typename _Tp::template rebind<_Up>::other;
2. allocator1
分配器是负责封装堆内存管理的对象。
2.1. 分配器
上图左侧。
C++的默认的内存分配器 std::allocator,继承至 __gnu_cxx::new_allocator。
2.1.1. __gnu_cxx::new_allocator
(1)对传入类型进行了类型萃取。
(2)rebind 重新绑定,定义 other 类型,用于萃取器萃取类型。
(3)封装实现分配对象内存、初始化对象、析构对象、释放对象内存,底层使用 new 和 delete。
address(): 用于获取分配地址allocate(): 用于分配内存deallocate(): 用于释放内存max_size(): 获取最大可分配数量construct(): 调用已分配内存对象的构造函数destroy(): 调用析构函数
2.1.2. std::allocator
(1)偏特化处理 void
(2)偏特化处理 const 和 volatile,重新形成有效的分配器类型
(3)类模板 std::allocator
rebind重新绑定,定义other类型,用于萃取器获取类型。
2.2. 萃取器
上图右侧。
类 __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits 继承于类std::allocator_traits,再继承于 std::__allocator_traits_base,用于获取内存分配器 allocator 的各个属性。
2.2.1. std::__allocator_traits_base
- 用于获取内存分配器
allocator的各个属性。
2.2.2. std::allocator_traits
私有函数模板
_S开头是封装对应名称分配器_Alloc原生的函数模板共有函数模板是封装自身对应名称
_S开头的私有函数模板有个特化版本是当
_Alloc是std::allocator,起别名后重复调用通用模板的共有函数模板
2.2.3. __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits
- 全部继承
std::allocator_traits,重载construct和destroy非标准类型指针 _S开头的静态函数是封装父类萃取类型
3. iterator2
迭代器是指向容器内元素的对象(如指针)。
3.1. 迭代器类型
上图中间。
3.1.1. std::iterator_tag
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
/// Marking input iterators.
struct input_iterator_tag { };
/// Marking output iterators.
struct output_iterator_tag { };
/// Forward iterators support a superset of input iterator operations.
struct forward_iterator_tag : public input_iterator_tag { };
/// Bidirectional iterators support a superset of forward iterator
/// operations.
struct bidirectional_iterator_tag : public forward_iterator_tag { };
/// Random-access iterators support a superset of bidirectional
/// iterator operations.
struct random_access_iterator_tag : public bidirectional_iterator_tag { };
STL库支持的迭代器类型是所有编程语言中最全面的,共有五种:
InputIterator: 输入迭代器。支持对容器元素的逐个遍历,以及对元素的读取(input);OutputIterator: 输出迭代器。支持对容器元素的逐个遍历,以及对元素的写入(output)。ForwardIterator: 前向迭代器。向前逐个遍历元素。可以对元素读取;BidirectionalIterator: 双向迭代器。支持向前向后逐个遍历元素,可以对元素读取。RandomAccessIterator: 随机访问迭代器。支持O(1)时间复杂度对元素的随机位置访问,支持对元素的读取。
这些是空类型用于区分不同的迭代器,区别不在于它们所包含的内容,而在于它们的是什么类型,然后可以基于不同迭代器类型支持的不同操作。
3.1.2. std::iterator
此类只定义嵌套的 typedef,子类迭代器类可以继承这个类以节省一些工作,然后用于特化和重载。
3.1.3. std::iterator_traits
此类只定义嵌套的 typedef,简单地从 Iterator 转发嵌套的 typedef 参数。 提供指针和指向常量的指针的特化版本。
3.2. 迭代器函数
上图左侧。
3.2.1. std::distance
计算迭代器之间的距离,通过一层类型判断确定 iterator_tag,然后转发给具体函数 __distance()。包括单向、随机。
3.2.2. std::advance
向前或向后移动迭代器,通过一层类型判断确定 iterator_tag,然后转发给具体函数 __advance()。包括单向、双向、随机。
next() 向后移动
prev() 向前移动
3.3. 衍生迭代器
上图右侧。
3.3.1. std::reverse_iterator
反向迭代器。
- 记录当前迭代器
- 重载操作运算符,
++内部实现为--,--内部实现为++等反向操作 - 该迭代器全局的各种重载操作运算符函数模板
3.3.2. std::back_insert_iterator
尾部插入迭代器。
- 记录一个容器,调用容器自己实现的
push_back() - 重载操作运算符,返回自身解引用
- 该迭代器全局的插入函数模板
3.3.3. std::front_insert_iterator
头部插入迭代器。
- 记录一个容器,调用容器自己实现的
push_front() - 重载操作运算符,返回自身解引用
- 该迭代器全局的插入函数模板
3.3.4. std::insert_iterator
插入迭代器。
- 记录一个容器,调用容器自己实现的
insert() - 重载操作运算符,返回自身解引用
- 该迭代器全局的插入函数模板
3.3.5. __gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator
这个迭代器适配器是一个普通的适配器,因为它不会改变迭代器参数的任何运算符的语义。它的主要目的是将不是类的迭代器(例如指针)转换为类迭代器。_Container 参数单独存在(不同容器),因此使用此模板的不同容器可以实例化不同的类型,即使 _Iterator 参数相同。
- 记录当前迭代器
- 重载操作运算符
- 该迭代器全局的各种重载操作运算符函数模板
3.3.6. std::move_iterator
类模板 move_iterator 是一个迭代器适配器,其行为与基础迭代器相同,只是其解引用运算符隐式将基础迭代的解引用运算符返回的值转换为右值引用。可以使用移动迭代器调用一些通用算法,以移动代替复制。
- 记录当前迭代器
- 重载操作运算符
- 该迭代器全局的各种重载操作运算符函数模板
4. vector
std::vector 是封装动态数组的顺序容器。连续存储元素,这意味着不仅可通过迭代器,还能用指向元素的常规指针访问元素。
4.1. 基类
std::_Vector_base 是基类,通过萃取获取分配类型和分配类型指针。
1
2
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type;
typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type>::pointer pointer;
具体保存数据结构。
1
2
3
4
5
6
struct _Vector_impl_data
{
pointer _M_start; // 起始指针
pointer _M_finish; // 实际空间结束指针
pointer _M_end_of_storage; // 分配空间结束指针
}
真正数据结构是 _Vector_impl,该结构多重继承于 _Vector_impl_data 和 _Tp_alloc_type(具体类型)实现封装管理内存调整(增加、收缩、删除)。
4.2. 具体类
std::vector 实现具体成员函数,实际都是对以下指针进行操作,部分进行迭代器封装。
1
2
3
_M_impl._M_start
_M_impl._M_finish
_M_impl._M_end_of_storage
例如 begin() end() empty() 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
/**
* Returns a read/write iterator that points to the first
* element in the %vector. Iteration is done in ordinary
* element order.
*/
iterator
begin() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_start); }
/**
* Returns a read/write iterator that points one past the last
* element in the %vector. Iteration is done in ordinary
* element order.
*/
iterator
end() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_finish); }
/**
* Returns true if the %vector is empty. (Thus begin() would
* equal end().)
*/
_GLIBCXX_NODISCARD bool
empty() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return begin() == end(); }
5. list
std::list 是支持常数时间从容器任何位置插入和移除元素的容器。不支持快速随机访问。它通常实现为双向链表。
5.1. 节点类型
节点类型分为以下三个:
_List_node_base: 基类节点,包含前向、后向指针。_List_node_header: 头节点,继承于_List_node_base,额外包含节点个数。_List_node: 数据节点,继承于_List_node_base,额外包含数据。
5.2. 基类
std::_List_node 是基类,该类的真正结构是 _List_impl,继承于 _List_node<_Tp>,内部包含 _List_node_header 头节点。std::_List_node 中声明 _List_impl 成员变量,操作都是对 _List_impl 成员变量中数据操作。
5.3. 具体类
std::list 实现具体成员函数,实际都是对以下指针进行操作,部分进行迭代器封装。
1
_M_impl._M_node
例如 begin() end() empty() 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
/**
* Returns a read/write iterator that points to the first element in the
* %list. Iteration is done in ordinary element order.
*/
iterator
begin() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_node._M_next); }
/**
* Returns a read/write iterator that points one past the last
* element in the %list. Iteration is done in ordinary element
* order.
*/
iterator
end() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return iterator(&this->_M_impl._M_node); }
/**
* Returns true if the %list is empty. (Thus begin() would equal
* end().)
*/
_GLIBCXX_NODISCARD bool
empty() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT
{ return this->_M_impl._M_node._M_next == &this->_M_impl._M_node; }
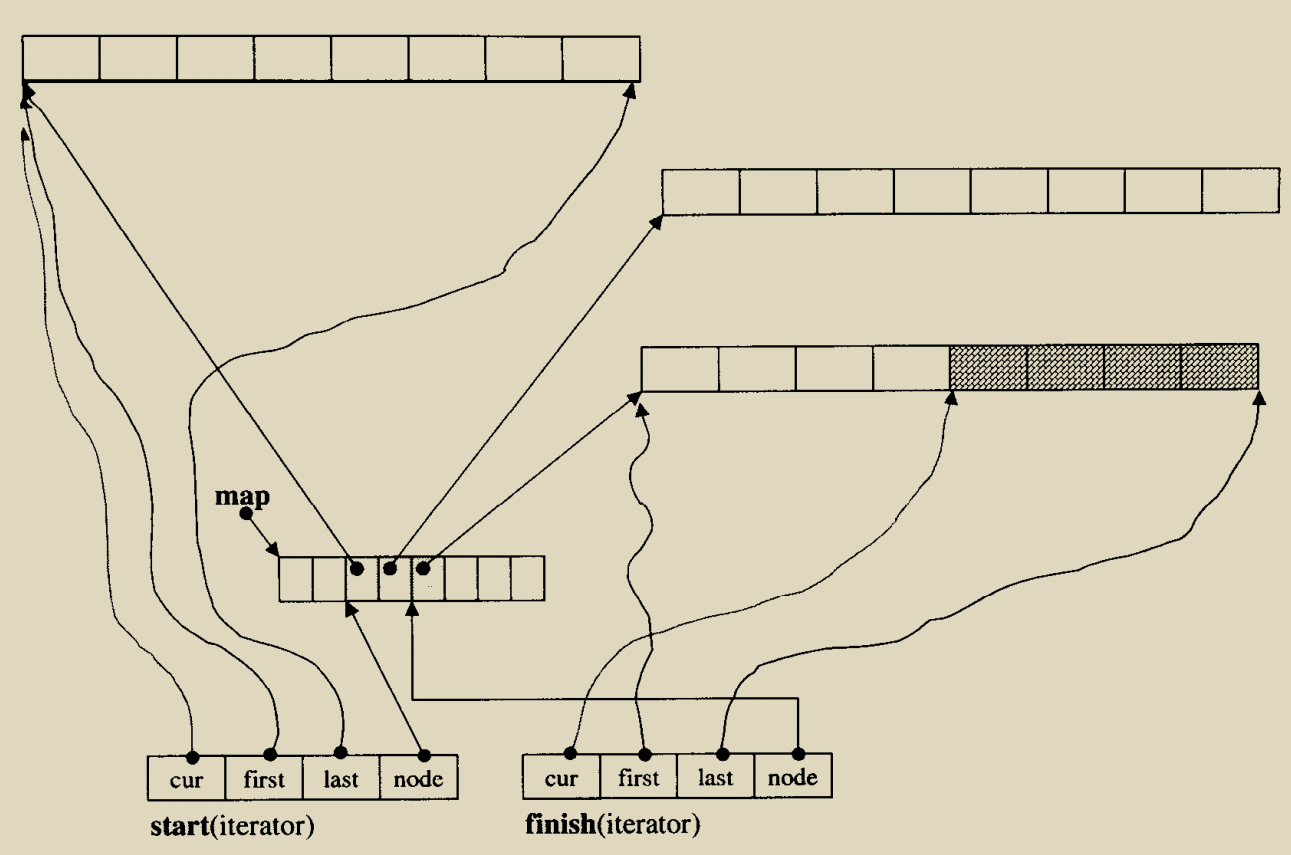
6. deque
std::deque(double-ended queue,双端队列)是有下标顺序容器,它允许在它的首尾两端快速插入及删除。另外,在 deque 任一端插入或删除不会使指向其余元素的指针或引用失效。
deque 的元素不是相接存储的:典型实现用单独分配的固定尺寸数组的序列,外加额外的序列,这表示下标访问必须进行二次指针解引用,与之相比 vector 的下标访问只进行一次。
6.1. 基类
std::_Deque_base 是基类,通过萃取获取分配类型和分配类型指针。
真正数据结构是 _Deque_impl,该结构继承于 _Tp_alloc_type(具体类型)实现封装管理内存调整(初始化、增加、删除)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
struct _Deque_impl
{
_Map_pointer _M_map; // 固定尺寸数组关联的序列
size_t _M_map_size; // 序列大小
iterator _M_start; // 起始迭代器
iterator _M_finish; // 终止迭代器
}
6.2. 具体类
std::deque 实现具体成员函数,实际都是对以下指针进行操作,部分进行迭代器封装。
1
2
_M_impl._M_start
_M_impl._M_finish
例如 push_front() push_back()函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
/**
* @brief Add data to the front of the %deque.
* @param __x Data to be added.
*
* This is a typical stack operation. The function creates an
* element at the front of the %deque and assigns the given
* data to it. Due to the nature of a %deque this operation
* can be done in constant time.
*/
void
push_front(const value_type& __x)
{
if (this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur != this->_M_impl._M_start._M_first)
{
_Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl,
this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur - 1,
__x);
--this->_M_impl._M_start._M_cur;
}
else
_M_push_front_aux(__x);
}
/**
* @brief Add data to the end of the %deque.
* @param __x Data to be added.
*
* This is a typical stack operation. The function creates an
* element at the end of the %deque and assigns the given data
* to it. Due to the nature of a %deque this operation can be
* done in constant time.
*/
void
push_back(const value_type& __x)
{
if (this->_M_impl._M_finish._M_cur
!= this->_M_impl._M_finish._M_last - 1)
{
_Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl,
this->_M_impl._M_finish._M_cur, __x);
++this->_M_impl._M_finish._M_cur;
}
else
_M_push_back_aux(__x);
}
7. 适配器
7.1. stack
std::stack 类是容器适配器,它给予程序员栈的功能——特别是 FILO(先进后出)数据结构。
适配器可以为标准容器 std::vector(包括 std::vector<bool>)、std::deque 和 std::list。如果没有为特定的 stack 类特化指定容器类,那么就会使用标准容器 std::deque。
实现方式一般是声明适配器变量,然后封装调用适配器容器函数来实现自己函数功能。例如 top() push()函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
template<typename _Tp, typename _Sequence = deque<_Tp> >
class stack
{
// 适配器容器 deque<_Tp>
_Sequence c;
/**
* Returns a read/write reference to the data at the first
* element of the %stack.
*/
reference
top()
{
__glibcxx_requires_nonempty();
return c.back();
}
/**
* @brief Add data to the top of the %stack.
* @param __x Data to be added.
*
* This is a typical %stack operation. The function creates an
* element at the top of the %stack and assigns the given data
* to it. The time complexity of the operation depends on the
* underlying sequence.
*/
void
push(value_type&& __x)
{ c.push_back(std::move(__x)); }
}
7.2. queue
std::queue 类是容器适配器,它给予程序员队列的功能——尤其是 FIFO (先进先出)数据结构。
适配器可以为标准容器 std::deque 和 std::list。
实现方式一般是声明适配器变量,然后封装调用适配器容器函数来实现自己函数功能。例如 push() pop()函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
template<typename _Tp, typename _Sequence = deque<_Tp> >
class queue
{
// 适配器容器 deque<_Tp>
_Sequence c;
/**
* @brief Add data to the end of the %queue.
* @param __x Data to be added.
*
* This is a typical %queue operation. The function creates an
* element at the end of the %queue and assigns the given data
* to it. The time complexity of the operation depends on the
* underlying sequence.
*/
void
push(value_type&& __x)
{ c.push_back(std::move(__x)); }
/**
* @brief Removes first element.
*
* This is a typical %queue operation. It shrinks the %queue by one.
* The time complexity of the operation depends on the underlying
* sequence.
*
* Note that no data is returned, and if the first element's
* data is needed, it should be retrieved before pop() is
* called.
*/
void
pop()
{
__glibcxx_requires_nonempty();
c.pop_front();
}
}
7.3. priority_queue
priority_queue 是容器适配器,它提供常数时间的(默认)最大元素查找,对数代价的插入与提取。
适配器可以为标准容器 std::vector(包括 std::vector<bool>)和 std::deque。
实现方式一般是声明适配器变量,然后封装调用适配器容器函数来实现自己函数功能。例如 top() pop()函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
template<typename _Tp, typename _Sequence = vector<_Tp>, typename _Compare = less<typename _Sequence::value_type> >
class priority_queue
{
// 适配器容器 vector<_Tp>
_Sequence c;
_Compare comp;
/**
* Returns a read-only (constant) reference to the data at the first
* element of the %queue.
*/
const_reference
top() const
{
__glibcxx_requires_nonempty();
return c.front();
}
/**
* @brief Removes first element.
*
* This is a typical %queue operation. It shrinks the %queue
* by one. The time complexity of the operation depends on the
* underlying sequence.
*
* Note that no data is returned, and if the first element's
* data is needed, it should be retrieved before pop() is
* called.
*/
void
pop()
{
__glibcxx_requires_nonempty();
std::pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);
c.pop_back();
}
}
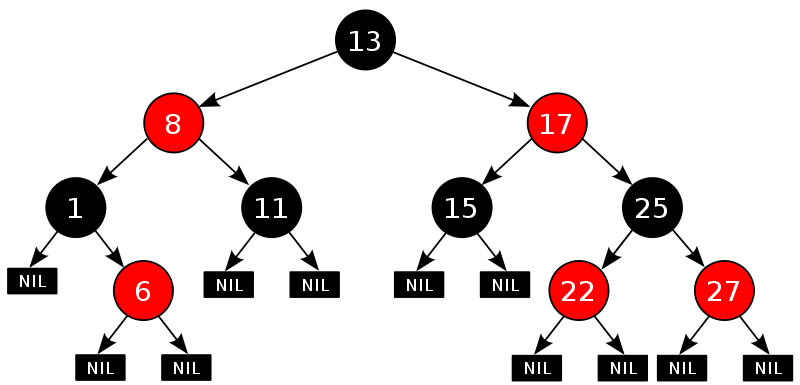
8. rb_tree
红黑树(英语:Red–black tree)是一种自平衡二叉查找树,红黑树是每个节点都带有颜色属性的二叉查找树,颜色为红色或黑色。在二叉查找树强制一般要求以外,对于任何有效的红黑树我们增加了如下的额外要求:
- 节点是红色或黑色。
- 根是黑色。
- 所有叶子都是黑色(叶子是NIL节点)。
- 每个红色节点必须有两个黑色的子节点。(或者说从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点。)(或者说不存在两个相邻的红色节点,相邻指两个节点是父子关系。)(或者说红色节点的父节点和子节点均是黑色的。)
- 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
8.1. set, multiset3
std::set 是关联容器,含有 Key 类型对象的已排序集。用比较函数 比较 (Compare) 进行排序。搜索、移除和插入拥有对数复杂度。set 通常以红黑树实现。
std::multiset 是含有 Key 类型对象有序集的容器。与 set 不同,它允许多个 Key 拥有等价的值。用关键比较函数 Compare 进行排序。搜索、插入和移除操作拥有对数复杂度。
8.2. map, multimap
std::map 是有序键值对容器,它的元素的键是唯一的。用比较函数 Compare 排序键。搜索、移除和插入操作拥有对数复杂度。map 通常实现为红黑树。
multimap 是关联容器,含有键值对的已排序列表,同时容许多个元素拥有同一键。按照应用到键的比较函数 Compare 排序。搜索、插入和移除操作拥有对数复杂度。拥有等价键的键值对的顺序就是插入顺序,且不会更改。
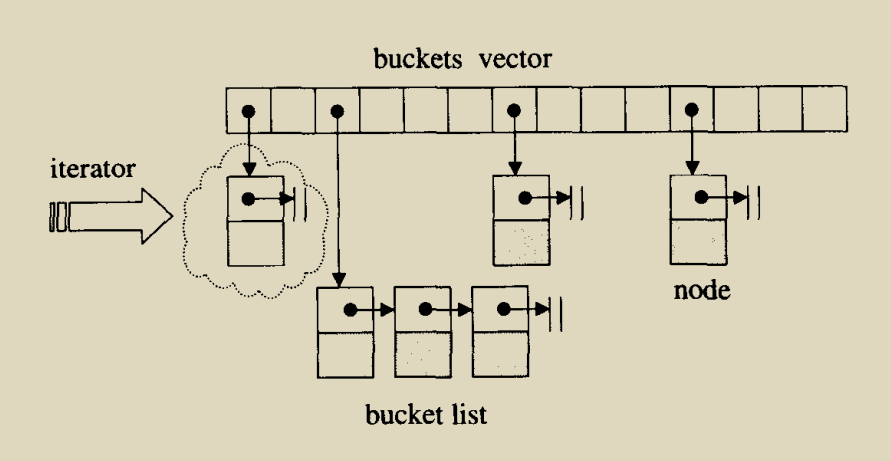
9. hashtable
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据键(Key)而直接访问在内存储存位置的数据结构。也就是说,它通过计算出一个键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来让人访问,这加快了查找速度。这个映射函数称做散列函数,存放记录的数组称做散列表。
9.1. unordered_set, unordered_multiset
unordered_set 是含有 Key 类型唯一对象集合的关联容器。搜索、插入和移除拥有平均常数时间复杂度。在内部,元素并不以任何特别顺序排序,而是组织进桶中。元素被放进哪个桶完全依赖其值的哈希。这允许对单独元素的快速访问,因为哈希一旦确定,就准确指代元素被放入的桶。不可修改容器元素(即使通过非 const 迭代器),因为修改可能更改元素的哈希,并破坏容器。
unordered_multiset 是关联容器,含有可能非唯一 Key 类型对象的集合。搜索、插入和移除拥有平均常数时间复杂度。不要求此容器的迭代顺序稳定。
9.2. unordered_map, unordered_multimap
unordered_map 是关联容器,含有带唯一键的键-值 pair 。搜索、插入和元素移除拥有平均常数时间复杂度。元素在内部不以任何特定顺序排序,而是组织进桶中。元素放进哪个桶完全依赖于其键的哈希。这允许对单独元素的快速访问,因为一旦计算哈希,则它准确指代元素所放进的桶。
unordered_multimap 是无序关联容器,支持等价的键(一个 unordered_multimap 可含有每个键值的多个副本)和将键与另一类型的值关联。 unordered_multimap 类支持向前迭代器。搜索、插入和移除拥有平均常数时间复杂度。不要求此容器的迭代顺序稳定。